Install the agent on Amazon EC2 and WorkSpaces
Deep Security Agent only supports Amazon WorkSpaces Windows desktops. There is no support for Linux desktops.
You can protect your existing Amazon EC2 instances and Amazon WorkSpaces with Deep Security as follows:
- Add your AWS accounts to Deep Security Manager
- Set the communication direction
- Configure the activation type
- Open ports
- Deploy agents to your Amazon EC2 instances and WorkSpaces
- Verify the agent installation and activation
- Assign a policy
If instead you want to launch new Amazon EC2 instances and Amazon WorkSpaces with the agent baked-in, see Install the agent on an AMI or WorkSpace bundle.
To protect Amazon WorkSpaces after already protecting your Amazon EC2 instances, see Protect Amazon WorkSpaces if you already added your AWS account.
Add your AWS accounts to Deep Security Manager
You need to add your AWS account or accounts to Deep Security Manager. These AWS accounts contain the Amazon EC2 instances and Amazon WorkSpaces that you want to protect with Deep Security.
See About adding AWS accounts for details.
After adding your AWS accounts:
- Your existing Amazon EC2 instances and Amazon WorkSpaces appear in Deep Security Manager. If no agent is installed on them, they appear with a Status of Unmanaged (Unknown) and a grey dot next to them. If an agent was already installed, they appear with a Status of Managed (Online) and green dot next to them.
- Any new Amazon EC2 instances or Amazon WorkSpaces that you launch through AWS under this AWS account are auto-detected by Deep Security Manager and displayed in the list of computers.
Set the communication direction
You are required to set the communication direction as either agent-initiated, manager-initiated, or bi-directional:
- Log in to Deep Security Manager.
- Set the communication direction by following instructions provided in Configure communication directionality and considering these guidelines:
- Agent/Appliance Initiated does not require you to open inbound ports on the Amazon EC2 instance or Amazon WorkSpace, while Bidirectional and Manager-Initiated do.
- Agent/Appliance Initiated is the safest option since no inbound ports need to be opened on the Amazon EC2 instance or Amazon WorkSpace.
- If you are using Amazon WorkSpaces, and you chose to set the communication direction to Bidirectional or Manager-Initiated, manually assign an elastic IP address to each WorkSpace before proceeding with further configurations. This gives the WorkSpace a public IP that can be contacted by Deep Security Manager. This is not required for EC2 instances because they already use public IP addresses. WorkSpaces use private IP addresses.
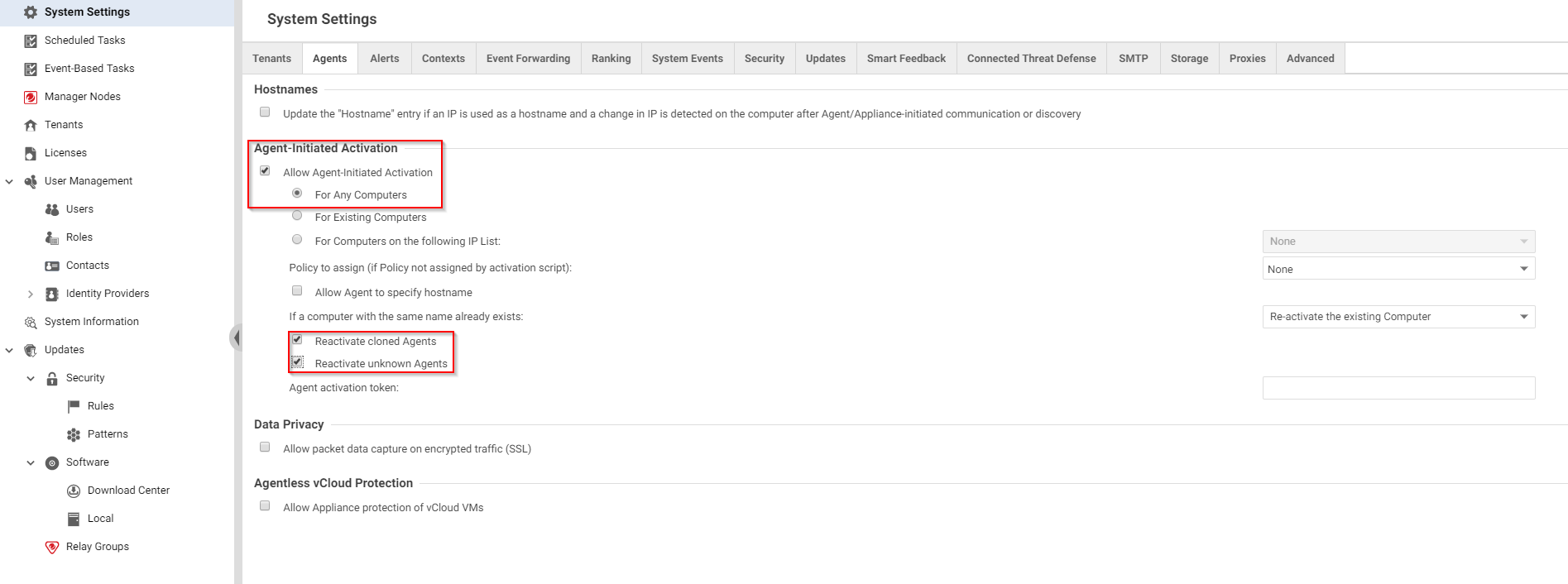
Configure the activation type
Activation is the process of registering an agent with a manager. You need to indicate whether or not to allow agent-initiated activation. If not, only manager-initiated activation is allowed.
- Log in to Deep Security Manager.
- Click Administration at the top.
- On the left, click System Settings.
- Ensure that the Agents tab is selected.
- Select or deselect Allow Agent-Initiated Activation, keeping in mind the following:
- Agent-initiated activation does not require you to open up inbound ports to your Amazon EC2 instances or Amazon WorkSpaces, while manager-initiated activation does.
- If agent-initiated activation is enabled, manager-initiated activation continues to work.
- Agent-initiated activation works even if you set the communication direction to Manager-Initiated.
- If you selected Allow Agent-Initiated Activation, also select Reactivate cloned Agents and Enable Reactivate unknown Agents. See Agent settings for more information.
- Click Save.
- If you are using Amazon WorkSpaces, and you did not allow agent-initiated activation, manually assign an elastic IP address to each WorkSpace now, before proceeding with further configurations. This gives each Amazon WorkSpace a public IP that can be contacted by other computers. This is not required for EC2 instances because they already use public IP addresses.
Open ports
You are required to make sure that the necessary ports are open to your Amazon EC2 instances or Amazon WorkSpaces.
- Open ports to your Amazon EC2 instances, as follows:
- Log in to your Amazon Web Services Console.
- Go to EC2 > Network & Security > Security Groups.
- Select the security group that is associated with your EC2 instances, then select Actions > Edit outbound rules.
- Open the necessary ports. For details, see Ports to open.
- Open ports to your Amazon WorkSpaces, as follows:
- Go to the firewall software that is protecting your Amazon WorkSpaces, and open the ports.
You have now opened the necessary ports so that Deep Security Agent and Deep Security Manager can communicate.
Ports to open
Typically:
- Agent-to-manager communication requires you to open the outbound TCP port (443 or 80, by default)
- Manager-to-agent communication requires you to open an inbound TCP port (4118).
Specifically:
- If you set the communication direction to Agent/Appliance-Initiated, open the outbound TCP port 443 or 80.
- If you set the communication direction to Manager-Initiated, open the inbound TCP port 4118.
- If you set the communication direction to Bidirectional, open both the outbound TCP port 443 or 80, as well as the inbound TCP port 4118.
- If you enabled Allow Agent-Initiated Activation, open the outbound TCP port 443 or 80 regardless of the communication direction.
- If you disabled Allow Agent-Initiated Activation, open the inbound TCP port 4118 regardless of the communication direction.
Deploy agents to your Amazon EC2 instances and WorkSpaces
You are required to deploy agents onto your Amazon EC2 instances and Amazon WorkSpaces by using one of the following options:
- Use a deployment script to install, activate, and assign a policy.
This is the best option if you need to deploy agents to many Amazon EC2 instances and Amazon WorkSpaces.
With this option, you must run a deployment script on the Amazon EC2 instances or Amazon WorkSpaces. The script installs and activates the agent and then assigns a policy. See Use deployment scripts to add and protect computers for details.
- Manually install and activate.
This is the best option if you only need to deploy agents to a few EC2 instances and Amazon WorkSpaces. You would need to perform the following:
- Get the Deep Security Agent software, copy it to the Amazon EC2 instance or Amazon WorkSpace, and then install it. For details, see Get Deep Security Agent software, and Install the agent.
- Activate the agent. You can do so on the agent (if the agent-initiated activation was enabled) or on Deep Security Manager. For details, see Activate the agent
You have now installed and activated Deep Security Agent on an Amazon EC2 instance or Amazon WorkSpace. A policy may or may not have been assigned, depending on the option you chose. If you chose to use a deployment script, a policy was assigned to the agent during activation. If you chose to manually install and activat the agent, then no policy has been assigned, and you need to assign one.
Verify the agent installation and activation
You should verify that your agent was installed and activated properly:
- Log in to Deep Security Manager.
- Click Computers at the top.
- On the left, make sure your Amazon EC2 instance or Amazon WorkSpace appears under Computers > your_AWS_account > your_region . Look for WorkSpaces in a WorkSpaces sub-node.
- In the main pane, make sure your Amazon EC2 instances or Amazon WorkSpaces appear with a Status of Managed (Online) and a green dot next to them.
Assign a policy
Skip this step if you ran a deployment script to install and activate the agent, as the script already assigned a policy so no further action is required.
If you installed and activated the agent manually, you must assign a policy to the agent. Assigning the policy sends the necessary protection modules to the agent so that your computer is protected.
To assign a policy, see Assign a policy to a computer.
After assigning a policy, your Amazon EC2 instance or Amazon WorkSpace is now protected.